- Recurrent Neurons
- RNN and HMM
- Backpropagation Through Time(BPTT)
- Gradient Vanishing / Gradient Exploding
- LSTM Cell
- GRU Cell
- Reference
递归神经网络主要有两类:一种是时间上的递归神经网络,一种是结构上的递归神经网络。RNN主要解决序列数据的处理,如文本、语音、视频等等。这类数据存在顺序关系,每个样本和它之前的样本存在关联。
Recurrent Neurons
Equation 1: output of sigle recurrent neuron for a single instance
\[y_{(t)} = \phi(x_{(t)}^{T} \cdot w_x + y_{t-1}^T \cdot w_y + b)\]- \(\phi\) 是激活函数,如ReLU,tanh。
Equation 2: outputs of a layer of recurrent neurons for all instances in a mini-batch
\[W = [\frac{W_x}{W_y}] \\ Y_{(t)} = \phi (X_{(t)} \cdot W_x + Y_{(t-1)} \cdot W_y + b) = \phi ([X_{(t)}Y_{(t-1)}] \cdot W + b)\]- \(Y_{(t)}\) 是 \(m \times n_{neurons}\) 的矩阵,表示的是step t时刻的输出。
- \(X_{(t)}\) 是 \(m \times n_{inputs}\) 的输入矩阵, \(n_{inputs}\)是输入feature的数量。
- \(W_x\) 是 \(n_{neurons} \times n_{inputs}\)大小,当前时间对的inputs权重矩阵。
- \(W_y\) 是 \(n_{neurons} \times n_{neurons}\)大小,上一时间output对当前输出的权重矩阵。
RNN and HMM
RNN的本质是一个数据推断(inference)机器, 只要数据足够多,就可以得到从\(x_{(t}\)到\(y_{(t)}\)的概率分布函数, 寻找到两个时间序列之间的关联,从而达到推断和预测的目的。这个很容易联想到另一个大名鼎鼎的模型-隐马尔科夫模型HMM(Hidden Markow Model)。z两者都是根据输入x推断输出y并维护一个隐变量,区别在于迁跃策略。RNN使用神经元连接矩阵,通过时间展开(时间递归部分,前向传播)和时间上反向传播进行迭代。HMM则使用更新状态转移矩阵来进行时间上的迭代。
HMM有三个典型(canonical)问题:
- 预测(filter):已知模型参数和某一特定输出序列,求最后时刻各个隐含状态的概率分布, 通常使用前向算法解决. 即求 \(P(x(t)\ |\ y(1),... ,y(t))\) .
- 平滑(smoothing):已知模型参数和某一特定输出序列,求中间时刻各个隐含状态的概率分布,通常使用forward-backward 算法解决. 即求 \(P(x(k)\ |\ y(1),... ,y(t)), (k<t)\) .
- 解码(most likely explanation): 已知模型参数,寻找最可能的能产生某一特定输出序列的隐含状态的序列, 通常使用Viterbi算法解决. 即求 \(P([x(1)\dots x(t)]|[y(1)\dots ,y(t)])\) .
Backpropagation Through Time(BPTT)
RNN的训练类似于ANN,也可以使用反向传播算法。首先,通过整个网络前向传播; 然后计算输出序列上的损失和梯度,损失函数表示为:\(C(Y_{(t_min)}, Y_{(t_min+1)}, ... ,Y_{(t_max)} )\)(仅计算\(t_{min}\)和\(t_{max}\)时间段); 接着将梯度反向传播到网络上所有的神经元上(不仅仅是最后一层上的神经元,计算损失和梯度相关时间上的神经元都需要更新)。
Gradient Vanishing / Gradient Exploding
RNN训练困难的主要原因再与隐藏层参数w传播过程时,无论在前向传播还是反向传播都会乘上多次。
许多人造神经网络(包括第一代RNNs网络),最终都遭受了严重的挫折——梯度消失问题。什么是梯度消失问题呢,其基本思想其实很简单。首先,来看一个梯度的概念,将梯度视为斜率。在训练深层神经网络的背景中,梯度值越大代表坡度越陡峭,系统能够越快地下滑到终点线并完成训练。但这也是研究者陷入困境的地方——当斜坡太平坦时,无法进行快速的训练。这对于深层网络中的第一层而言特别关键,因为若第一层的梯度值为零,说明没有了调整方向,无法调整相关的权重值来最下化损失函数,这一现象就是“消梯度失”。随着梯度越来越小,训练时间也会越来越长,类似于物理学中的沿直线运动,光滑表面,小球会一直运动下去。
LSTM Cell
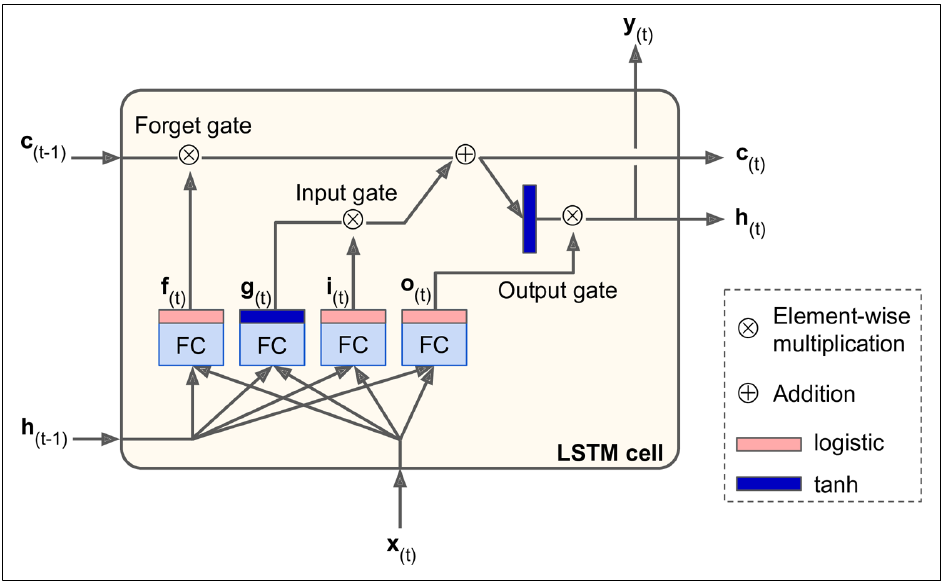
LSTM Cell从外部看类似于Basic Cell,但是内部多了一些控制门,表现比Basic Cell要好。LSTM cell最主要的特点是多了一个显式记忆矩阵(Long term memory部分,可称之为cell state vector)和调整进出信息的三个门(input/output/forget gate)。
In short, an LSTM cell can learn to recognize an important input (that’s the role of the input gate), store it in the long-term state, learn to preserve it for as long as it is needed (that’s the role of the forget gate), and learn to extract it whenever it is needed. This explains why they have been amazingly successful at capturing long-term patterns in time series, long texts, audio recordings, and more.
Papers
先补一下论文:
“Long Short-Term Memory,” S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber (1997).
“Recurrent Neural Network Regularization,” W. Zaremba et al. (2015).
Introduction of the LSTM model:
Addition of the forget gate to the LSTM model:
More recent LSTM paper:
Papers related to Theano:
- Bastien, Frédéric, Lamblin, Pascal, Pascanu, Razvan, Bergstra, James, Goodfellow, Ian, Bergeron, Arnaud, Bouchard, Nicolas, and Bengio, Yoshua. Theano: new features and speed improvements. NIPS Workshop on Deep Learning and Unsupervised Feature Learning, 2012.
- Bergstra, James, Breuleux, Olivier, Bastien, Frédéric, Lamblin, Pascal, Pascanu, Razvan, Desjardins, Guillaume, Turian, Joseph, Warde-Farley, David, and Bengio, Yoshua. Theano: a CPU and GPU math expression compiler. In Proceedings of the Python for Scientific Computing Conference (SciPy), June 2010.
Main layer
这一层和普通cell一样计算,通过当前输入和上一时间的隐藏层计算产生新的信息输出。
\[g_{(t)} = tanh(W_{xg}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hg}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)} + b_g )\]Input Gate
控制哪些输入信息加入到计算。
\[i_{(t)} = \phi(W_{xi}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hi}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)} + b_i)\]Forget Gate
控制哪些信息需要被丢弃。
\[f_{(t)} = \phi(W_{xf}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hf}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)} + b_f)\]Output Gate
控制哪一部分信息需要读取但是其输出需要丢弃。
\[o_{(t)} = \phi(W_{xo}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{ho}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)} + b_o)\]Cell state Vector
是网络的memory部分输出。其更新由两部分决定:上一次的记忆(通过forget gate决定上一次记忆哪部分需要被遗忘丢弃)和新的信息(通过main layer算出新的信息,通过input gate决定哪部分信息加入计算)。
\[c(t) = f_{(t)} \otimes c_{(t-1)} + i_{(t)} \otimes g_{(t)}\]Output
输出经过output gate控制决定哪部分信息可以输出到下一层(下一时刻)。
\[y_{(t)} = h_{(t)} = o_{(t)} \otimes tanh(c_{(t)})\]LSTM Training
- BPTT 反向传播还是最常用算法
- 需要学习的weights包括:
- Input/Output/Forget Gates
- Input tanh layer (main layer)
- 输出则取决于任务类型,一般RNN上是一段数据后输出一个label比如翻译、单词联想。
Deep LSTM
提到深度,基本上都是堆处理层(摊手)。
GRU Cell
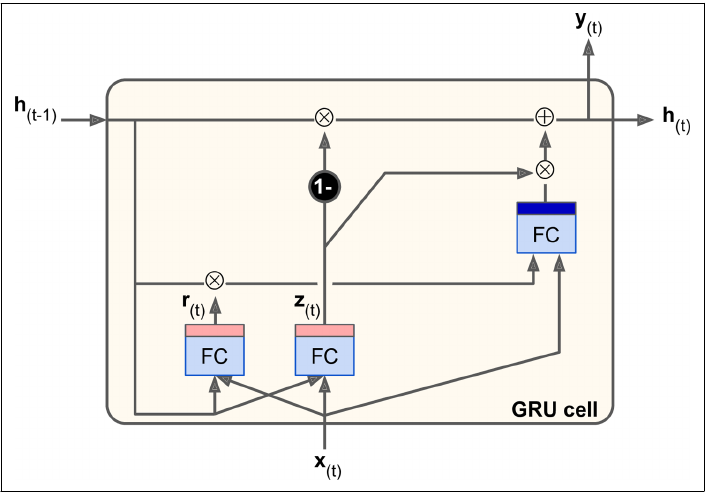
Gated Recurrent Unit(GRU,paper在此https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555)可以认为是LSTM的一个简化版,并且表现好像还差不多。简化的部分:
- 将input和foreget gate简化为一个update gate,如update gate为1时,input开forget关,为0则相反。
- 将输出的cell state和hidden state合并为一个,并增加一个新的gate控制上一次哪些信息加入到main layer计算。
合并的gate \(z_{(t)}\) 将用于控制输入和上一次的信息,达到input/forget门控制类似的效果。
\[z_{(t)} = \phi (W_{xz}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hz}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)})\]新增的gate \(r_{(t)}\) 仅用于控制上一次的信息哪些加入计算。
\[r_{(t)} = \phi (W_{xr}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hr}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)})\]main layer中参与计算的输入信息(memory)\(h_{(t-1)}\)的受控于\(r_{(t)}\)。
\[g_{(t)} = tanh(W_{xg}^T \cdot x_{(t)} + W_{hg}^T \cdot (r_{(t)} \otimes h_{(t-1)} ) )\]输出时\(z_{(t)}\)对新增的信息\(g_{(t)}\)和上一次信息\(h_{(t-1)}\)进行融合。
\[h_{(t)} = (1-z_{(t)}) \otimes h_{(t-1)} + z_{(t)} \otimes g_{(t)}\]“Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-learn and Tensorflow-Page405” 书中公式貌似有错,有待考证
\[h_{(t)} = (1-z_{(t)}) \otimes tanh(W_{xg}^T \cdot h_{(t-1)} + z_{(t)} \otimes g_{(t)})\]